Blood sugar regulation isn’t just a concern for those diagnosed with diabetes—it’s a critical factor in overall health. When glucose levels become too high, the body sends warning signals, many of which people overlook or dismiss as unrelated symptoms. Understanding these signs early can help prevent severe health complications.
In this article, we’ll explore 12 key symptoms of high blood sugar, why they happen, and how you can restore balance naturally.
What Is Blood Sugar and Why Does It Matter?
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, is the body’s primary source of energy. It fuels cells and ensures proper function. The hormone insulin, produced by the pancreas, helps regulate blood glucose by moving it into cells where it can be used for energy.
However, when this process is disrupted—either due to insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production—glucose remains in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar (hyperglycemia). Over time, this can damage organs, nerves, and blood vessels, increasing the risk of serious conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and kidney failure.
12 Symptoms of High Blood Sugar You Should Never Ignore
1. Constant Thirst
Excess glucose in the bloodstream draws water from the body’s tissues, leading to dehydration. As a result, you may experience persistent dry mouth and an unquenchable thirst, even if you’re drinking plenty of fluids.
✔ What to do: Increase water intake, avoid sugary drinks, and consume more electrolyte-rich foods like coconut water and leafy greens.
2. Frequent Urination

Excess sugar in the blood forces the kidneys to work harder to filter it out, leading to frequent trips to the bathroom—especially at night.
✔ What to do: Stay hydrated and avoid processed carbohydrates, which spike glucose levels.
3. Extreme Hunger (Even After Eating)
When insulin resistance prevents glucose from entering the cells, the body feels starved and signals hunger, even if you’ve just eaten.
✔ What to do: Include fiber, protein, and healthy fats in meals to slow glucose absorption and keep you full longer.
4. Fatigue and Weakness

Glucose is the body’s primary energy source, but if cells can’t absorb it, energy levels plummet, leading to persistent fatigue and weakness.
✔ What to do: Prioritize protein-rich foods, low-glycemic fruits, and regular movement to maintain stable energy levels.
5. Blurred Vision
Excess sugar can pull fluid from the lenses of your eyes, leading to swelling and blurred vision. If left untreated, chronic hyperglycemia can damage the retina and lead to permanent vision impairment.
✔ What to do: Monitor blood sugar levels and consume foods rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, such as spinach, kale, and carrots, to support eye health.
6. Slow-Healing Wounds and Bruises
High blood sugar affects circulation and damages small blood vessels, slowing down the body’s ability to heal wounds or fight infections.
✔ What to do: Consume foods high in vitamin C and zinc to support immune function and wound healing.
7. Frequent Infections
A weakened immune system makes you more susceptible to infections, including urinary tract infections (UTIs), gum disease, and yeast infections.
✔ What to do: Reduce processed sugar intake, consume probiotic-rich foods, and ensure you get enough vitamin D for immune support.
8. Numbness and Tingling in Hands & Feet
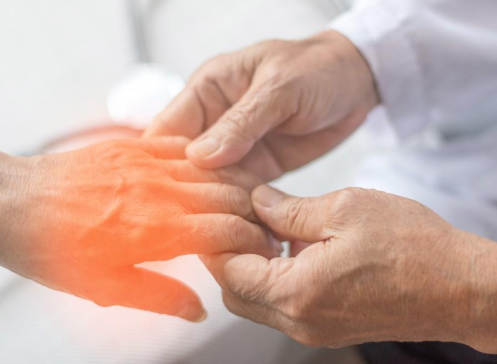
Nerve damage from chronic high blood sugar—a condition known as diabetic neuropathy—can cause tingling, burning, or numbness in extremities.
✔ What to do: Manage blood sugar naturally with anti-inflammatory foods, such as turmeric, ginger, and omega-3-rich foods like salmon.
9. Mood Swings and Irritability
Fluctuations in blood sugar levels impact hormones and neurotransmitters, leading to anxiety, depression, and sudden mood swings.
✔ What to do: Balance blood sugar with high-protein meals, adaptogenic herbs, and stress management techniques like deep breathing.
10. Dry Skin and Mouth
Dehydration caused by high blood sugar reduces natural skin moisture, leading to itchiness, dry patches, and an increased risk of skin infections.
✔ What to do: Increase healthy fats like avocado and nuts, stay hydrated, and use natural moisturizers like coconut oil.
👇 To continue reading, scroll down and click Next 👇





