Papillomaviruses are infectious agents that belong to the group of viruses known as “naked” (because they lack a lipid layer surrounding them), and are made up of a protein layer that envelops the DNA-like genetic material. These viruses affect certain species. The human papillomavirus is characterized by affecting the skin and mucous membranes in various parts of the human body. It is of medical importance due to its ability to cause certain types of neoplasia, but not all have this ability. Let’s take a look at them in detail.
Human papillomaviruses are divided into two large groups based on common genetic characteristics. First, we have low-risk viruses, which cause warts in various areas of the body and are rarely associated with malignant lesions. Secondly, there are high-risk or oncogenic viruses, capable of producing lesions that, if left untreated, can develop into cancer, in both men and women, including cervical cancer and cancer of other anatomical areas, genitals, and throat.
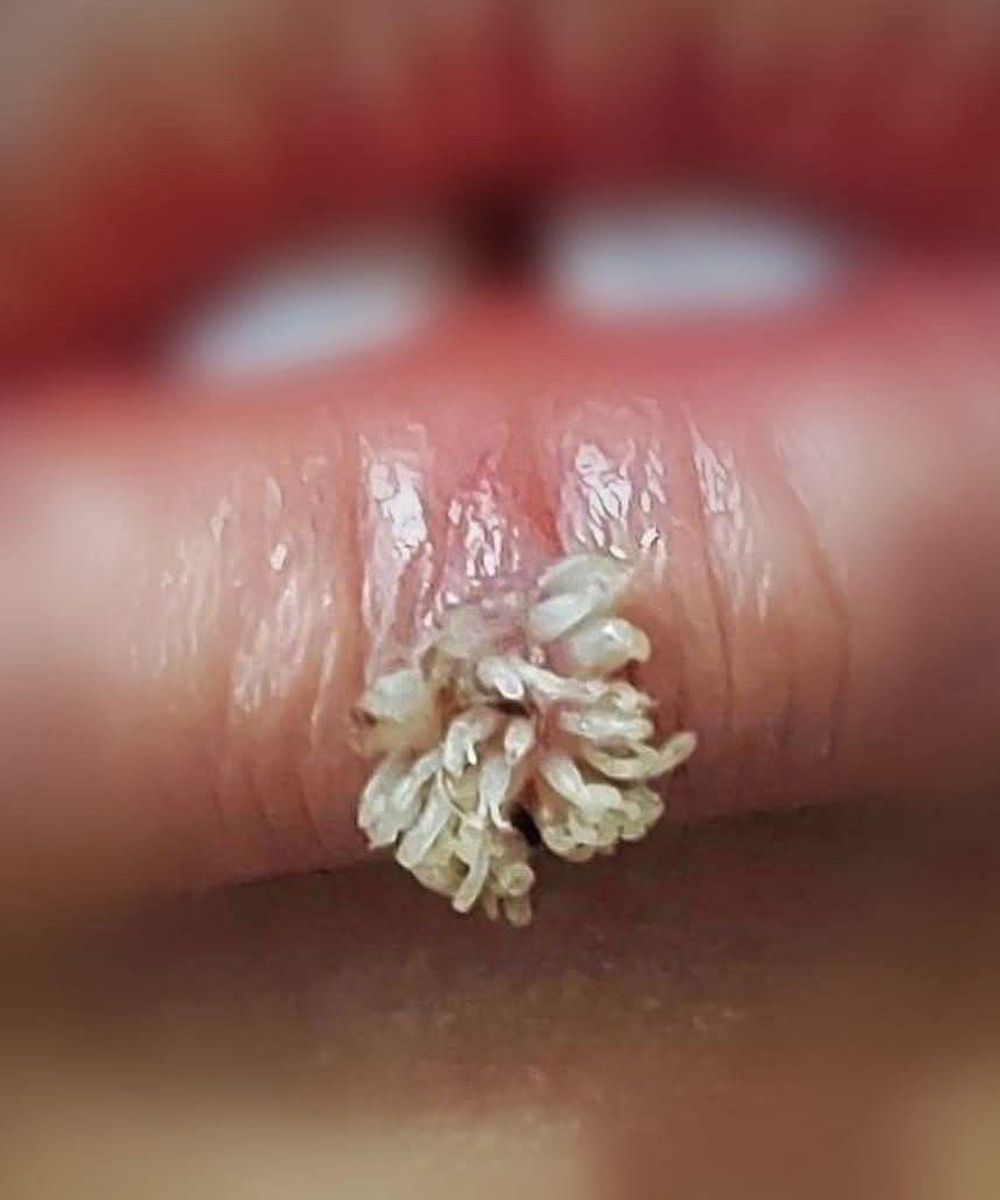
The lesions they produce can be classified according to their clinical characteristics into five types:
Common wart. Commonly caused by types 2 and 4 (low risk)
Flat wart. Caused by types 2, 3, and 5 (low risk)
Plantar wart. Caused by types 1, 2, 4, and 10
Genital wart (condyloma acuminata), usually caused by types 6 and 11, considered low risk, or one of the oncogenic types, including 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, and 39
Premalignant and malignant lesions and cancer. They are mainly caused by high-risk HPV types 16 and 18.
All good, but how can I contract the virus?
CONTINUE READING NEXT PAGE