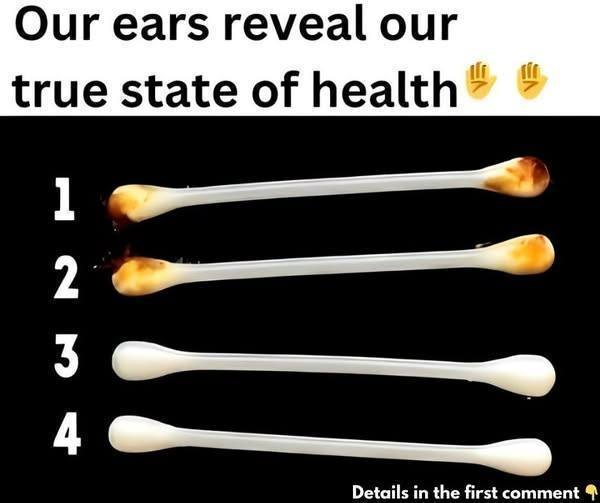
In the hierarchy of bodily functions, earwax—medically termed cerumen—rarely receives the credit it deserves. Far from being a mere “hygiene nuisance,” this waxy secretion is a biological marvel. Produced by specialized glands in the outer ear canal, cerumen acts as a self-cleaning agent with antifungal and antibacterial properties.1 It traps debris, lubricates the delicate skin of the canal, and …
👇 👇 👇 👇 👇