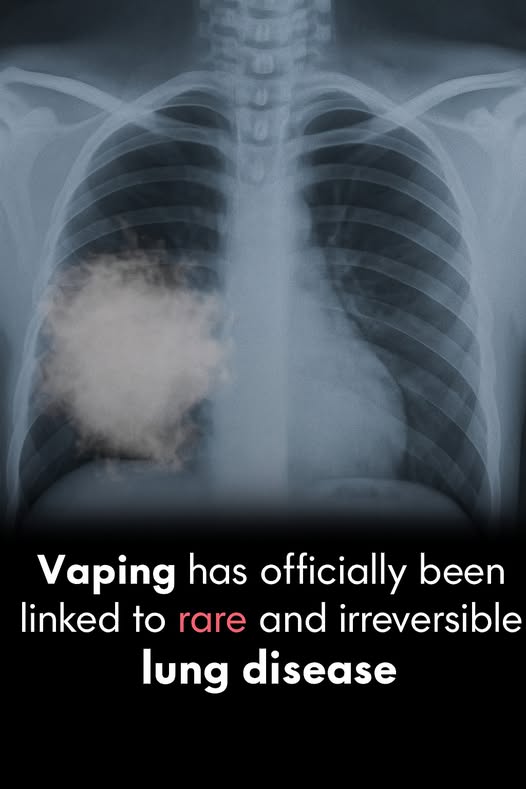
For years, vaping has been marketed as a “cleaner,” “safer” alternative to traditional smoking — a modern, tech-savvy way to satisfy nicotine cravings without the tar and smoke.
But mounting scientific evidence is painting a different picture.
Even nicotine-free e-cigarettes may be doing silent, invisible damage — not just to your lungs, but to your blood vessels, circulation, and long-term vitality.
A groundbreaking study from the University of Pennsylvania reveals that all forms of vaping impair blood flow and oxygen delivery — and the damage begins after just one session.
It’s time to look beyond the flavored vapor and understand the real risks.
1. Vaping Damages Blood Flow — Even Without Nicotine
In a revealing study, researchers examined 31 healthy adults (ages 21–49) — including smokers, vapers, and non-users — using MRI scans to measure blood flow before and after inhaling:
Traditional cigarette smoke
Nicotine-containing e-cigarette vapor
Nicotine-free e-cigarette vapor
The results?
👉 All three methods significantly reduced blood flow in the superficial femoral artery — a major vessel in the thigh that supplies oxygen to the lower body.
Even more alarming:
Oxygen delivery dropped across the board
Blood vessels showed impaired function within minutes
These effects were not reversed quickly — suggesting real, acute vascular stress
This means:
You don’t need nicotine to harm your circulatory system.
The act of vaping itself — the heated aerosol, the chemical byproducts — is enough to constrict blood vessels and reduce oxygen flow.
2. It’s Not Just Nicotine — It’s the Chemistry of Vaping
While nicotine is addictive and harmful, it’s not the only villain in e-cigarettes.
When the e-liquid is heated by the device’s metal coil, it produces a cocktail of toxic compounds, including:
🔥 Formaldehyde & Acrolein
Carcinogenic chemicals formed when e-liquids overheat
Irritate and damage lung tissue and airways
Linked to chronic bronchitis and reduced lung function
⚗️ Heavy Metals (Lead, Nickel, Chromium)
Leached from the metal coils during heating
Accumulate in the body over time
Harmful to neurological, respiratory, and cardiovascular systems
🌫️ Ultrafine Particles
Inhaled deep into the lungs
Trigger inflammation and oxidative stress
Can enter the bloodstream and affect organs
Even flavorings like diacetyl (used in buttery flavors) have been linked to “popcorn lung” — a serious lung disease.