The antidote should ideally be administered within the first hour. After six hours, its effectiveness decreases and irreversible tissue damage may occur.
How can you tell if the snake was poisonous?
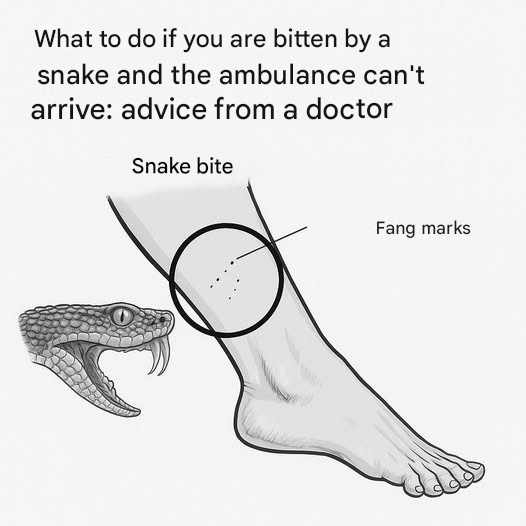
- Venomous snakes usually leave two well-defined fang marks .
- Non-poisonous ones leave more diffuse traces, similar to scratches.
- The moment of the bite may not hurt much, especially if it happens over clothing.
Why are some cases mild and others severe?
- The amount of venom depends on whether the snake has already bitten before or if it released its entire reserve in the attack.
- Running, moving around a lot, or panicking facilitates the spread of the poison.
- The person’s age and general health also influence the reaction to the poison.
Types of poison and their effects
- Hemotoxic : like those of the viper, they cause tissue damage, necrosis and coagulation problems.
- Neurotoxins : like those of cobras, they affect the nervous system and can paralyze breathing.
In rural areas of South America, hemotoxic poisons are prevalent. Although rarely fatal, they can cause serious long-term effects if not treated promptly.